Erfolgsgeschichten
Alle ErfolgsgeschichtenCSP offers premium network services backed by topology-aware transport assurance
EXFO helps a Tier 1 European CSP build faster, more dependable networks to improve its revenue streams
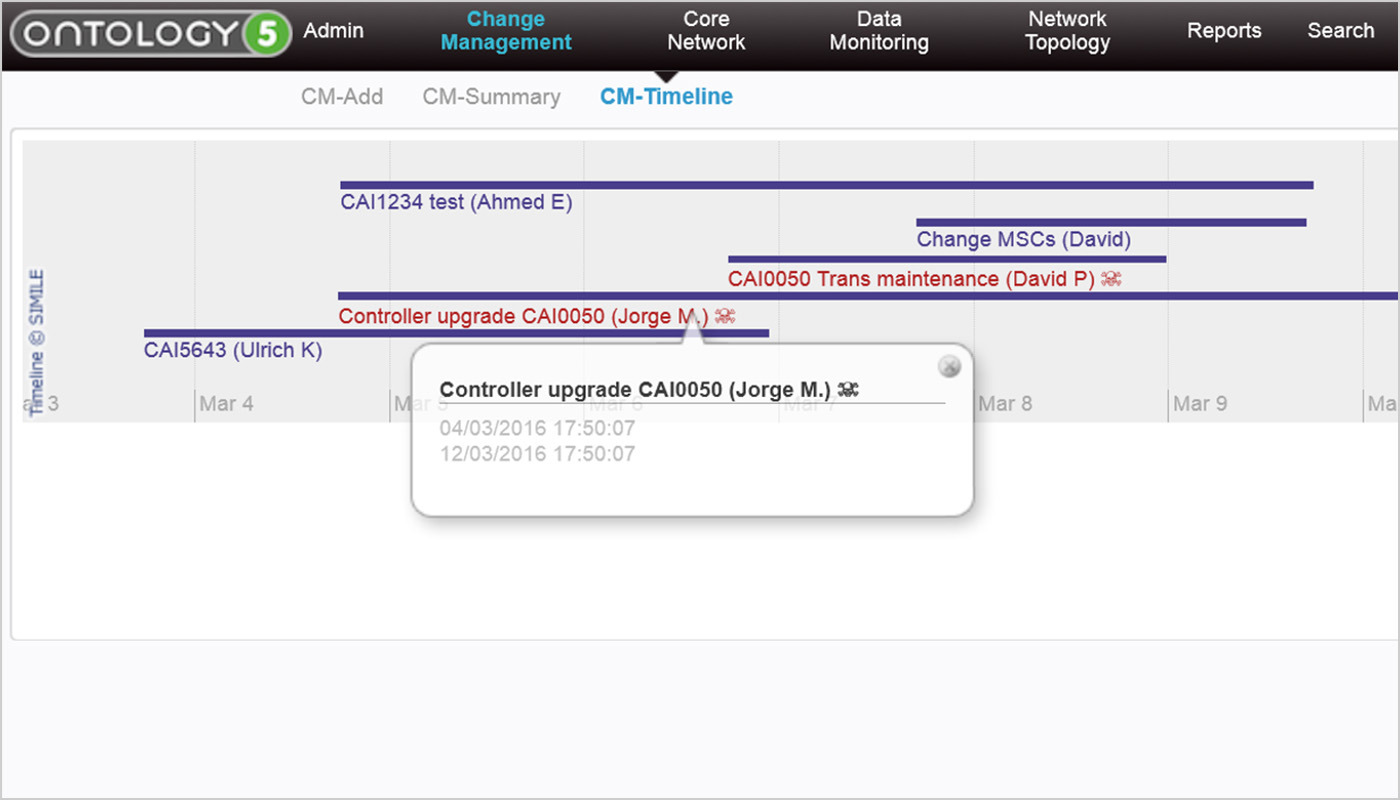
European operator uses Nova Context to improve trouble-ticket management
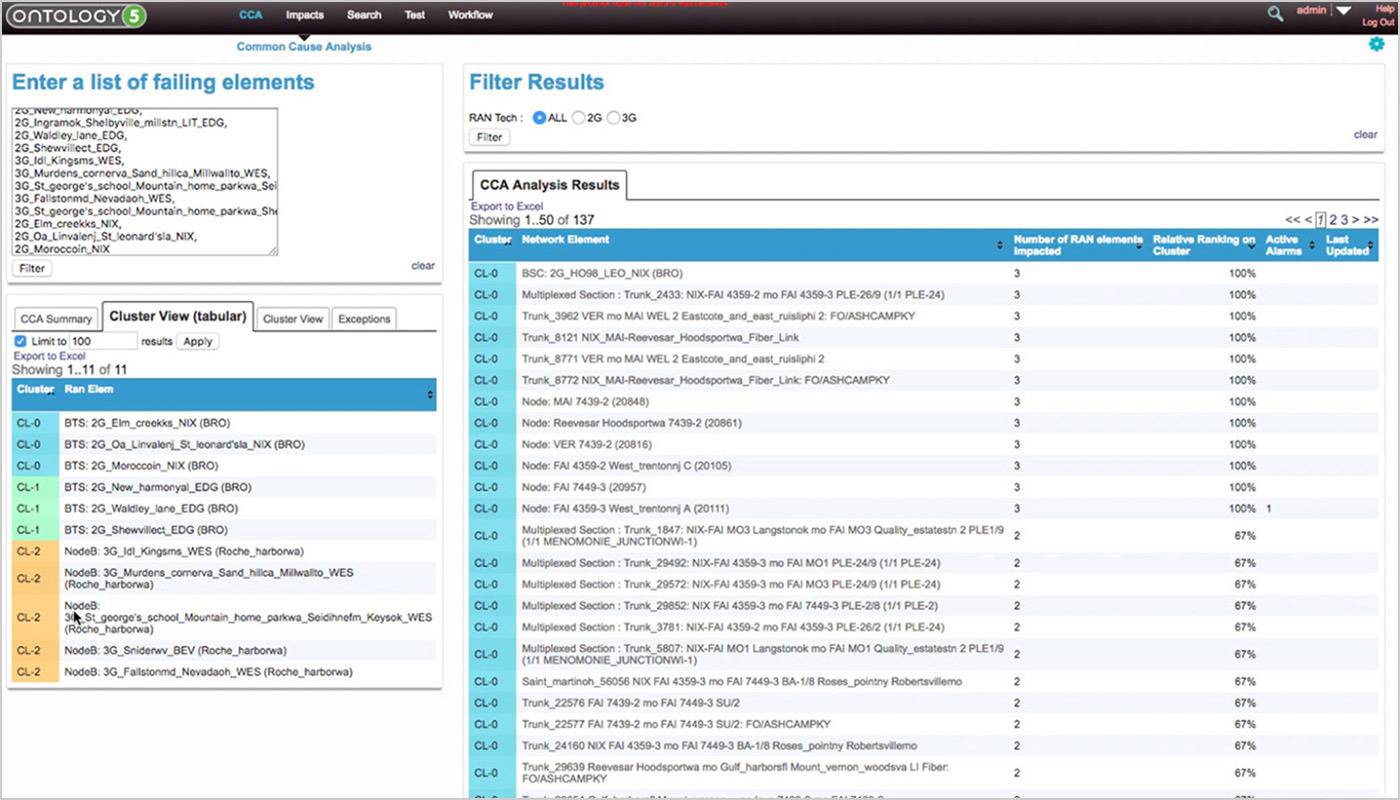
In order to power its new OSS/BSS processes, a European MNO selected EXFO’s Nova Context (formerly EXFO Ontology’s) service impact analysis (SIA) and common cause analysis modules to improve customer trouble-ticket management by ranking repairs according to business priorities.
CenturyLink automates service delivery with EXFO's real-time topology
Telenor enhances the experience of its business customers
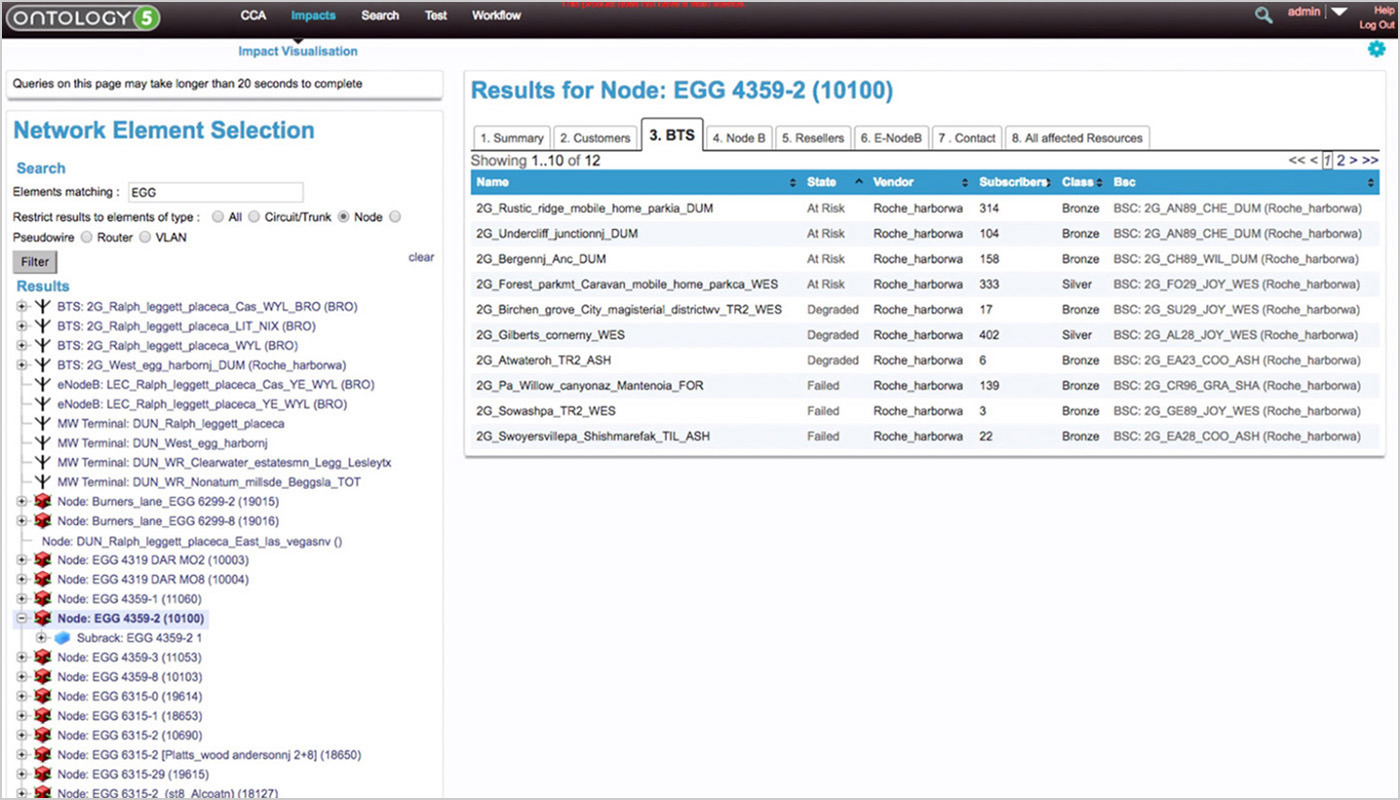
Reducing impact on customers during network upgrades
Nova Context - Customer 360 platform
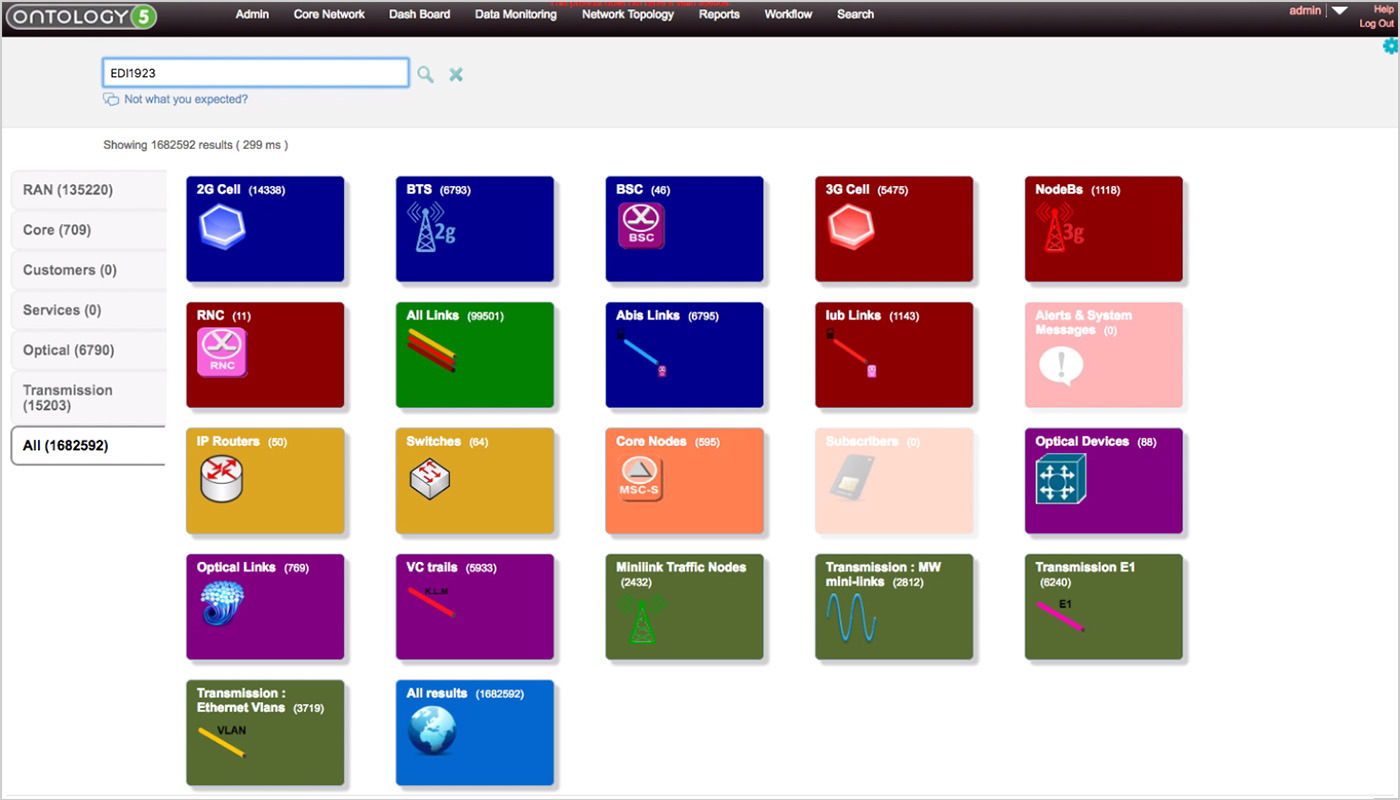
Equipping a leading CSP to easily and quickly visualize accurate customer service topologies
Stratecast Solution Strategies: Multiple Views, Not Multiple Versions at Telkom South Africa
Tackling inventory consolidation issues